One of the most prevalent forms of cancer that affects men is prostate cancer. Recognizing the early signs, understanding the causes and risk factors, and knowing the preventive measures are crucial in managing prostate cancer effectively.
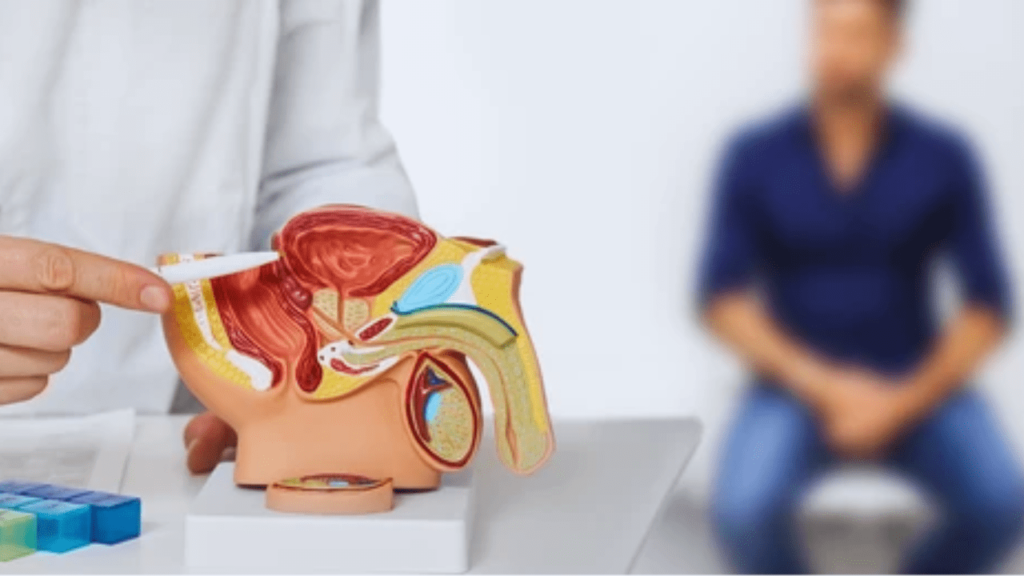
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces seminal fluid, which nourishes and transports sperm. This type of cancer is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate gland. Prostate cancer can range from being slow-growing and confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause significant harm, to being aggressive and spreading quickly to other parts of the body.
Symptoms
Prostate cancer in its early stages often presents no symptoms. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may become more noticeable. Common symptoms of prostate cancer include:
- Frequent Urination: Especially at night (nocturia).
- Difficulty Starting Urination: A weak or interrupted flow of urine.
- Painful Urination: Discomfort or a burning sensation during urination.
- Blood in Urine or Semen: Hematuria and hematospermia, respectively.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Inability to get or keep an erection.
- Painful Ejaculation: Discomfort during ejaculation.
- Discomfort in the Pelvic Area: Persistent pain or stiffness in the lower back, hips, or thighs.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: A sudden, unexplained drop in weight.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of non-cancerous conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostatitis. Therefore, a proper medical evaluation is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Causes
The exact cause of prostate cancer remains unknown. However, several factors can contribute to the development of this disease. Understanding these factors can help in recognizing the potential risks and seeking early intervention.
- Genetic Mutations: Changes in the DNA of prostate cells can lead to uncontrolled cell growth. These genetic changes may be inherited or occur spontaneously.
- Hormonal Imbalances: High levels of androgens, particularly testosterone, can stimulate the growth of prostate cancer cells.
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, particularly after the age of 50.
- Family History: Men with a family history of prostate cancer or other cancers (such as breast cancer) are at a higher risk.
- Race and Ethnicity: Prostate cancer is more common in African American men and less common in Asian American and Hispanic men.
- Diet and Lifestyle: A diet high in red meat, processed foods, and dairy products may increase the risk, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats may reduce the risk.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Certain chemicals, such as those found in pesticides, can increase the risk of prostate cancer.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase a man’s chances of developing prostate cancer. While some of these factors are beyond control, others can be managed to reduce the overall risk.
- Age: The risk of prostate cancer increases significantly with age, particularly after the age of 50.
- Family History: A history of prostate cancer in immediate family members, such as a father or brother, increases the risk.
- Race and Ethnicity: African American men have a higher risk of developing prostate cancer and are more likely to have aggressive forms of the disease. The reasons for this are not entirely clear but may involve genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic Factors: Inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, which are more commonly associated with breast cancer, can also increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Diet: A diet high in red meat, processed foods, and dairy products, and low in fruits and vegetables, may increase the risk of prostate cancer.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese has been linked to an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to obesity and other health issues, indirectly increasing the risk of prostate cancer.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer and other cancers.
SUGGESTED: Breast Cancer Awareness 2024: Discover Early Symptoms & Detection to Empower Precious Lives!
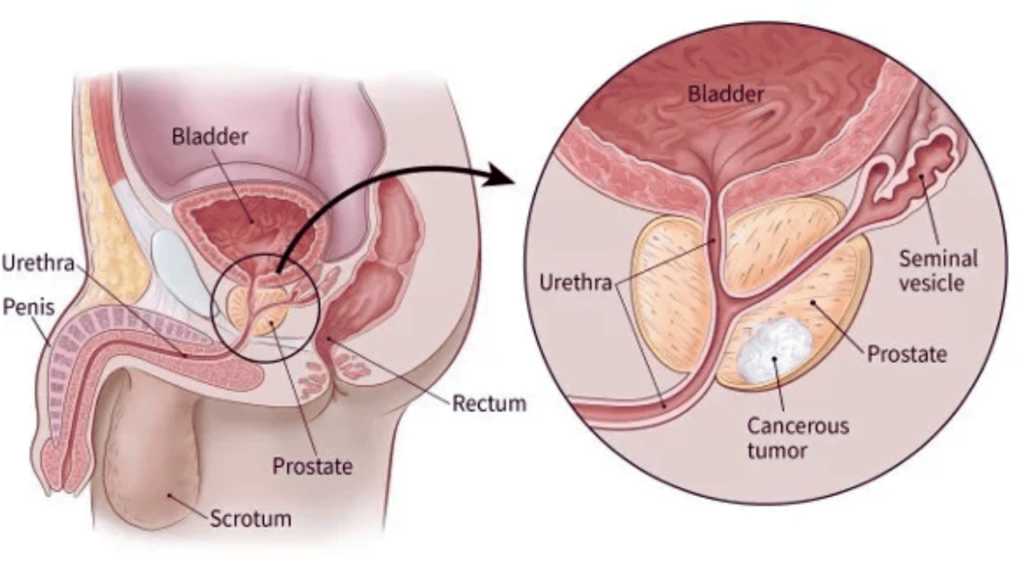
Complications
Prostate cancer and its treatment can lead to several complications, impacting the quality of life and overall health.
- Metastasis: Prostate cancer can spread to nearby organs, such as the bladder, or travel through the bloodstream or lymphatic system to bones or other organs. Bone metastasis can cause severe pain and fractures.
- Incontinence: Both prostate cancer and its treatment can affect bladder control, leading to urinary incontinence. Treatment options for incontinence include medications, catheters, and surgery.
- Erectile Dysfunction: Treatments such as surgery, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy can cause erectile dysfunction. Medications, vacuum devices, and surgery can help manage this condition.
- Bowel Dysfunction: Radiation therapy can irritate the rectum, leading to bowel problems such as diarrhea, rectal bleeding, or discomfort.
- Psychological Impact: The diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, and depression. Mental health treatments, therapy, and support groups might be helpful.
Prevention Tips
While there’s no sure way to prevent prostate cancer, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk. Some preventative steps that can be done include:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in red and processed meats can help reduce the risk of prostate cancer. Foods high in antioxidants, such as tomatoes (which contain lycopene), green tea, and broccoli, may be particularly beneficial.
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and lowering the risk of prostate cancer can be achieved by frequent physical activity. Strive for 30 minutes or more of moderate activity most days of the week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of aggressive prostate cancer. It’s critical to maintain a healthy weight with regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Avoid Smoking: Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of various cancers, including prostate cancer.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of prostate cancer. Limiting alcohol intake to moderate levels is advisable.
- Regular Screening: Regular prostate cancer screening can help detect the disease early when it is more treatable. Discuss with your doctor the best time to start screening, especially if you have risk factors.
A Quick Review
Prostate cancer is a significant health issue that affects many men worldwide. Understanding the symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, and preventive measures is crucial for early detection and effective management.
By adopting a healthy lifestyle and staying informed, men can reduce their risk of prostate cancer and improve their overall well-being.
Read Next:
The Psychology of Love: Why Valentines Day Matters More Epic Than You Think
Discover the psychology of love and why Valentines Day is more important than you think. Learn how love impacts the brain, strengthens relationships, and boosts

Premier League Highlights: Arsenal Humiliate Man City 5-1, Spurs and Palace Secure Crucial Wins
Arsenal demolished Manchester City 5-1 in a statement premier league highlights win, reigniting their title hopes. Meanwhile, Crystal Palace stunned Man United 2-0, and Tottenham

How Budget 2025 Impacts the Indian Middle-Class: Major Tax Benefits and Glaring Omissions
Budget 2025 offers major tax relief to the middle class, including zero tax on incomes up to ₹12 lakh. However, it misses out on incentives

Degrees vs Employability: Why “Highly Qualified Degree Holders” Struggle to Find Jobs While “Less Qualified Individuals” Get Hired Faster!
Many highly qualified individuals struggle to secure jobs, while less qualified candidates get hired quickly. This Degrees vs Employability paradox is caused by employer preferences,

The Power of Mindset: Why Looking Poor Doesn’t Make You Poor, but Thinking Poor Does!
Discover why looking poor doesn’t define your wealth but thinking poor does. Learn the power of mindset and how a growth-oriented mindset can lead to

Overthinking: How It’s Damaging Today’s Youth – Causes and Cure in 2025
Understanding how overthinking is silently damaging today’s youth, from its causes rooted in societal pressure and social media to its long-term effects on mental health.

Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose: An Epitome of Epic Leadership
Discovering the incredible life of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose, a leader whose vision, courage, and determination redefined India’s freedom struggle. Explore his leadership qualities, ideology,

Global News Headlines Today: From Gaza Ceasefire to Blue Origin’s Massive 2025 Milestone
Explore today’s top global news headlines, from the Gaza ceasefire and Blue Origin’s historic spaceflight to Apple losing its top spot in China’s smartphone market.

The Hidden Danger of Social Media Nudity: A Threat to Today’s Youth in 2025
Understanding how social media nudity is impacting the youth and their future potential. Learn about the risks of unregulated content, cultural sensitivities, and solutions for

FA Cup 2024: Manchester United Survive Arsenal Test to Advance in FA Cup Fourth Round
Manchester United defeated Arsenal in a thrilling FA Cup third-round encounter, with Atlay Bayindir’s heroics sealing the win. Read about key moments, standout performances, and

Supercopa de España: Barcelona Dominate Real Madrid 5-2 to Claim Supercup
Barcelona delivered a stunning 5-2 victory over Real Madrid in the Supercopa de España final. Read about the key moments, star players, and the significance

Global News Highlights Today: India’s Metro Milestone, US Aid Shift, iOS Stunning Updates and More!
Explore today’s global news highlights, including the Tibet earthquake, political tensions in South Korea, LA wildfires, US aid shifts, and India’s metro milestone. Stay informed

The Power of Keeping Plans Private in 2025: Why Silence is the Key to Achieving Your Dreams!
Discover why keeping plans private is crucial for achieving your dreams. Learn how silence boosts focus, protects momentum, and helps you achieve success without distractions

Rolls-Royce Ghost Series II Arrives in India 2025: Elegance Meets Stunning Innovation
Discover the all-new Rolls-Royce Ghost Series II launched in India, priced from ₹8.95 crore. Explore its stunning design, luxurious interior, enhanced tech features, and powerful

Global News Highlights: Earthquakes in Tibet, US Bird Flu Crisis Fatality, Brics Welcomes Indonesia in 2025, and Many more
Explore this week’s global news highlights, including the first bird flu death in the US, Indonesia joining Brics, devastating earthquakes in Tibet, rising HMPV cases
