According to the IDF Diabetes Atlas (2021), 10.5% of adults (20–79 years old) have diabetes, and nearly half of them are not aware that they have the disease. IDF forecasts indicate that by 2045, 1 in 8 adults, or 783 million, will have diabetes—a 46% rise.

In today’s fast-paced world, where convenience often takes precedence over health, it’s crucial to shed light on a silent epidemic that affects millions worldwide: diabetes. With the right knowledge and proactive measures, diabetes can be managed effectively, enabling individuals to lead fulfilling lives. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the essentials of diabetes, focusing on early detection, precautions, and care. Additionally, we’ll explore basic exercises and dietary tips crucial for maintaining optimal diabetes levels.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, stems from the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar.
Primarily there are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
- Type 1 Diabetes: Often diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require insulin injections for survival.
- Type 2 Diabetes: More prevalent than Type 1, Type 2 diabetes typically develops in adulthood and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity. When a person has Type 2 diabetes, their body either stops producing enough insulin to keep their blood sugar levels normal or develops resistant to it.
Early Detection Saves Lives
Effective diabetes management and the avoidance of complications depend heavily on early detection. Recognizing the symptoms and undergoing regular screenings can make a significant difference. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst and hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in extremities
[If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly for proper diagnosis and management.]

Precautions and Care
Managing diabetes requires a holistic approach encompassing lifestyle modifications, medication adherence (if prescribed), and regular monitoring. Here are some essential precautions and care tips:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-carb snacks.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity plays a pivotal role in diabetes management by improving insulin sensitivity and promoting weight loss. Along with strength training, try to get in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider. Keep track of fluctuations and adjust your lifestyle or medication accordingly.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration and support optimal bodily functions.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-relieving activities like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or hobbies.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep to support overall health and regulate hormones involved in blood sugar control.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking exacerbates diabetes-related complications and increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. If you are currently smoking, get help to stop.
Basic Exercises and Foods for Diabetes Management
Incorporating the following exercises and foods into your routine can help maintain proper diabetes levels:
Exercises:
- Walking: A low-impact exercise accessible to most individuals, walking improves cardiovascular health and aids in weight management.
- Cycling: Cycling is an excellent aerobic exercise that strengthens muscles, improves endurance, and enhances insulin sensitivity.
- Yoga: Practicing yoga promotes relaxation, flexibility, and stress reduction, all of which are beneficial for diabetes management.
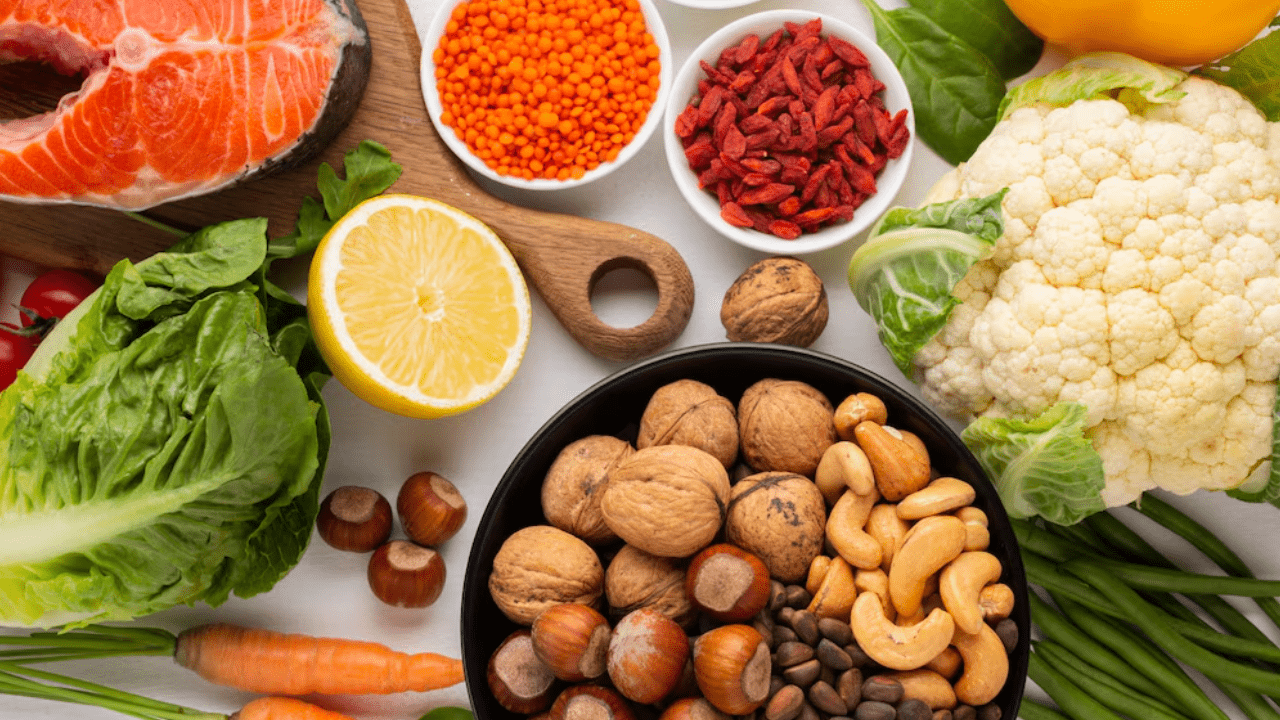
Foods:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are rich in nutrients and low in calories, making them ideal for managing blood sugar levels.
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats, which provide fiber and help stabilize blood sugar.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources such as chicken breast, tofu, and legumes into your meals to promote satiety and blood sugar control.
- Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil in moderation to support heart health and enhance insulin sensitivity.

By embracing a proactive approach to diabetes management, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and enjoy an improved quality of life. Keep in mind that over time, little lifestyle adjustments can have a big impact. For individualized advice and assistance throughout your diabetes journey, speak with your healthcare practitioner.
In conclusion, understanding diabetes, early detection, precautions, and care are pivotal in effectively managing this chronic condition. By adopting a holistic approach encompassing healthy lifestyle choices, regular exercise, and mindful eating, individuals can empower themselves to live well with diabetes.
Read Next:
The Psychology of Love: Why Valentines Day Matters More Epic Than You Think
Discover the psychology of love and why Valentines Day is more important than you think. Learn how love impacts the brain, strengthens relationships, and boosts

Premier League Highlights: Arsenal Humiliate Man City 5-1, Spurs and Palace Secure Crucial Wins
Arsenal demolished Manchester City 5-1 in a statement premier league highlights win, reigniting their title hopes. Meanwhile, Crystal Palace stunned Man United 2-0, and Tottenham

How Budget 2025 Impacts the Indian Middle-Class: Major Tax Benefits and Glaring Omissions
Budget 2025 offers major tax relief to the middle class, including zero tax on incomes up to ₹12 lakh. However, it misses out on incentives
