Tianlong-3 rocket crashed during a ground test, dealing a serious blow to China’s commercial rocket sector.
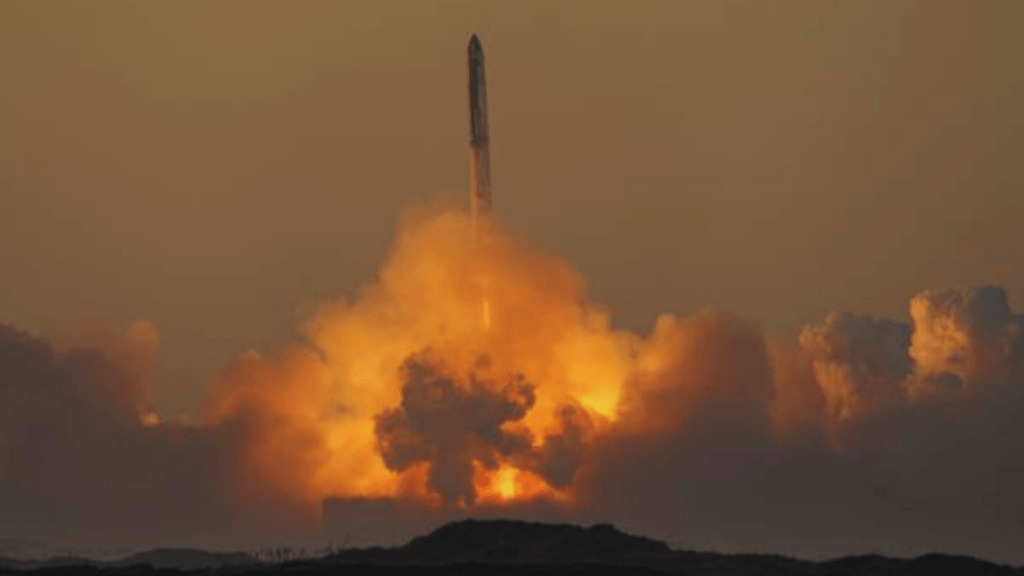

In a shocking turn of events on Sunday, the Tianlong-3 rocket crashed during a ground test, dealing a serious blow to China’s commercial rocket sector. The incident occurred due to an accidental launch, according to Space Pioneer, the company behind the rocket.
The crash, reported by CNN, happened when the first stage of the Tianlong-3 rocket detached from its launch pad because of a structural failure. This mishap is a blow to Space Pioneer, a leading company in the commercial rocket sector, which specializes in liquid-propellant rockets.
Details of the Incident
The incident took place in Gongyi city, located in central China. As stated by Space Pioneer, the failure happened when the rocket body’s connection to the test platform broke. As a result, the launch pad and first-stage rocket separated. After liftoff, the rocket crashed into a hilly terrain 1.5 kilometers (0.9 miles) southwest of the test platform due to an automatic shutdown of the onboard computer. The rocket disintegrated upon impact.
Fortunately, there were no injuries reported as people in the area were evacuated in advance of the rocket test. This precautionary measure ensured the safety of the local population despite the unexpected failure.
Space Pioneer’s Statement
Space Pioneer, formerly Beijing Tianbing Technologies, stressed that the accident’s main cause was a structural failure between the rocket body and the test platform. The first-stage rocket was removed from the launch pad as a result of the structural failure of the connection between the rocket body and the test platform, according to their official statement. The rocket plunged 1.5 kilometers southwest of the test platform into the steep mountains as the onboard computer automatically shut down after liftoff. The rocket body broke apart after colliding with the mountain.
This incident is a significant setback for Space Pioneer, which had successfully launched its Tianlong-2 rocket in April 2023. The Tianlong-2 launch marked China’s first commercial launch of a liquid carrier rocket into orbit, showcasing Space Pioneer’s capabilities and ambitions in the commercial space sector.
Implications for Space Pioneer and China’s Space Ambitions
China’s satellite internet network was supposed to be built with the assistance of the gigantic liquid carrier rocket Tianlong-3, which crashed on Sunday. Space Pioneer has ambitious plans for the Tianlong-3, claiming that its performance is comparable to SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. The company aims to achieve over 30 launches per year once the rocket successfully completes its maiden flight.
The accident comes at a time when China’s space ambitions are soaring. Just days before the Tianlong-3 crash, China celebrated the return of its Chang’e-6 lunar module, which brought back the first-ever samples from the far side of the moon. This mission is a key milestone in China’s long-term goal, as articulated by Chinese leader Xi Jinping, to establish the country as a dominant space power.
The Road Ahead for Space Pioneer
Space Pioneer, a prominent player among China’s burgeoning private-sector rocket manufacturers, has been a significant contributor to the country’s space exploration efforts since private investment was permitted in China’s space industry in 2014. With the goal of cutting mission costs, a multitude of commercial space firms have arisen, concentrating on the development of reusable rockets and satellite production.
The Tianlong-3 rocket, designed with two stages and partially reusable, represents a significant technological advancement for Space Pioneer. However, the recent accident highlights the inherent risks and challenges in developing cutting-edge space technology.
Safety Measures and Future Testing
Although there have been previous instances of rocket debris landing in China after a launch, it is extremely uncommon for a developmental rocket stage to separate from its testing platform and crash beyond the test site. This incident underscores the importance of stringent safety measures and rigorous testing protocols in the commercial space industry.
Space Pioneer operates its testing center in Gongyi, Henan Province, an inland area with a population of 800,000. Unlike many other companies that have established test sites along China’s coasts for safety reasons, Space Pioneer’s inland testing location presents unique challenges and risks. Ensuring the safety of local populations and preventing similar incidents in the future will be crucial for the company’s continued success.
Summary
The Tianlong-3 rocket crash is a stark reminder of the complexities and risks associated with space exploration and rocket development. As Space Pioneer investigates the cause of the structural failure and works to prevent future incidents, the company’s resilience and commitment to advancing China’s space capabilities will be tested. This incident, while a setback, also serves as an opportunity for Space Pioneer to refine its technologies and enhance safety measures, ultimately contributing to the growth and success of China’s commercial space industry.
Read Next:
The Psychology of Love: Why Valentines Day Matters More Epic Than You Think
Discover the psychology of love and why Valentines Day is more important than you think. Learn how love impacts the brain, strengthens relationships, and boosts

Premier League Highlights: Arsenal Humiliate Man City 5-1, Spurs and Palace Secure Crucial Wins
Arsenal demolished Manchester City 5-1 in a statement premier league highlights win, reigniting their title hopes. Meanwhile, Crystal Palace stunned Man United 2-0, and Tottenham

How Budget 2025 Impacts the Indian Middle-Class: Major Tax Benefits and Glaring Omissions
Budget 2025 offers major tax relief to the middle class, including zero tax on incomes up to ₹12 lakh. However, it misses out on incentives

Degrees vs Employability: Why “Highly Qualified Degree Holders” Struggle to Find Jobs While “Less Qualified Individuals” Get Hired Faster!
Many highly qualified individuals struggle to secure jobs, while less qualified candidates get hired quickly. This Degrees vs Employability paradox is caused by employer preferences,

The Power of Mindset: Why Looking Poor Doesn’t Make You Poor, but Thinking Poor Does!
Discover why looking poor doesn’t define your wealth but thinking poor does. Learn the power of mindset and how a growth-oriented mindset can lead to

Overthinking: How It’s Damaging Today’s Youth – Causes and Cure in 2025
Understanding how overthinking is silently damaging today’s youth, from its causes rooted in societal pressure and social media to its long-term effects on mental health.
